LoRA 用于语义相似性任务
译者:片刻小哥哥
项目地址:https://huggingface.apachecn.org/docs/peft/task_guides/semantic-similarity-lora
原始地址:https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/task_guides/semantic-similarity-lora
低秩适应(LoRA)是一种重参数化方法,旨在减少具有低秩表示的可训练参数的数量。权重矩阵被分解为经过训练和更新的低秩矩阵。所有预训练的模型参数保持冻结。训练后,低秩矩阵被添加回原始权重。这使得存储和训练 LoRA 模型更加高效,因为参数明显减少。
💡阅读 LoRA:大型语言模型的低秩适应 了解有关 LoRA 的更多信息。
在本指南中,我们将使用 LoRA
脚本
微调一个
intfloat/e5-large-v2
模型上的
smangrul/amazon_esci
语义相似性任务的数据集。请随意探索该脚本,以更详细地了解其工作原理!
设置
首先安装 🤗 PEFT 来源 ,然后导航到包含用于使用 LoRA 微调 DreamBooth 的训练脚本的目录:
cd peft/examples/feature_extraction
使用以下命令安装所有必需的库:
pip install -r requirements.txt
接下来,导入所有必需的库:
- 🤗 用于加载的变压器
intfloat/e5-large-v2模型和分词器 - 🤗 加速训练循环
- 🤗 用于加载和准备的数据集
smangrul/amazon_esci用于训练和推理的数据集 - 🤗 Evaluate 用于评估模型的性能
- 🤗 PEFT 用于设置 LoRA 配置并创建 PEFT 模型
- 🤗 Huggingface_hub 用于将训练好的模型上传到 HF hub
- hnswlib 用于创建搜索索引并进行快速近似最近邻搜索
假设已经安装了支持 CUDA 的 PyTorch。
火车
启动训练脚本
‘加速发射’
并传递你的超参数
--use_peft
启用 LoRA 的参数。
本指南使用以下内容 LoraConfig :
peft_config = LoraConfig(
r=8,
lora_alpha=16,
bias="none",
task_type=TaskType.FEATURE_EXTRACTION,
target_modules=["key", "query", "value"],
)
以下是在具有标准 RAM 的 V100 GPU 上的 Colab 中运行时,完整的脚本参数集可能如下所示:
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" peft_lora_embedding_semantic_search.py --dataset_name="smangrul/amazon\_esci" --max_length=70 --model_name_or_path="intfloat/e5-large-v2" --per_device_train_batch_size=64 --per_device_eval_batch_size=128 --learning_rate=5e-4 --weight_decay=0.0 --num_train_epochs 3 --gradient_accumulation_steps=1 --output_dir="results/peft\_lora\_e5\_ecommerce\_semantic\_search\_colab" --seed=42 --push_to_hub --hub_model_id="smangrul/peft\_lora\_e5\_ecommerce\_semantic\_search\_colab" --with_tracking --report_to="wandb" --use_peft --checkpointing_steps "epoch"
语义相似度数据集
我们将使用的数据集是数据集的一小部分
esci-data
数据集(可以在 Hub 上找到
smangrul/amazon_esci
)。
每个样本包含一个元组
(查询、产品标题、相关性标签)
在哪里
相关性标签
是
1
如果产品符合意图
查询
,否则就是
0
。
我们的任务是构建一个嵌入模型,可以在给定产品查询的情况下检索语义相似的产品。 这通常是构建产品搜索引擎以检索给定查询的所有潜在相关产品的第一阶段。 通常,这涉及使用双编码器模型来交叉连接查询和数百万个可能会迅速爆炸的产品。 相反,您可以使用 Transformer 模型来检索给定查询的前 K 个最接近的相似产品: 将查询和产品嵌入到同一潜在嵌入空间中。 数以百万计的产品被离线嵌入以创建搜索索引。 在运行时,模型仅嵌入查询,并使用搜索索引从搜索索引中检索产品
快速近似最近邻搜索库,例如 FAISS 或者 HNSWlib 。
下一阶段涉及对检索到的产品列表重新排序以返回最相关的产品; 此阶段可以利用基于交叉编码器的模型作为查询和有限的一组检索产品之间的交叉连接。 下图来自 真棒语义搜索 概述了一个粗略的语义搜索管道:
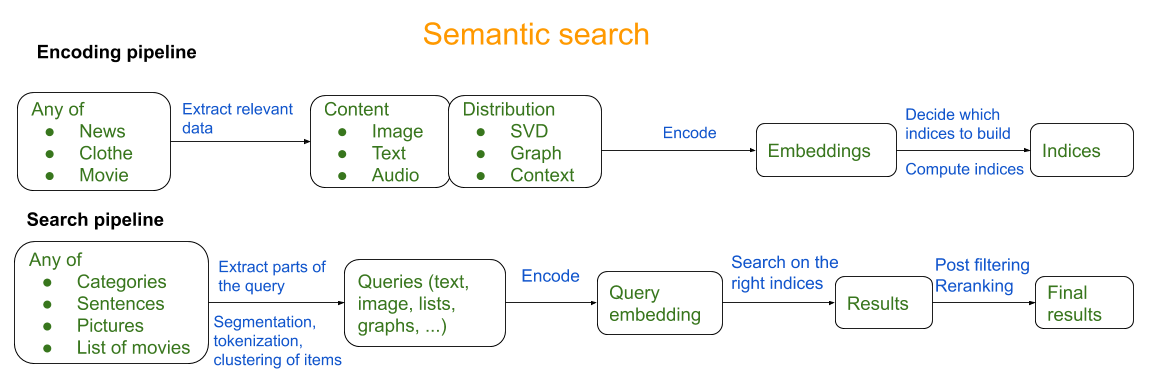
对于本任务指南,我们将探索训练嵌入模型以预测语义相似产品的第一阶段 给出产品查询。
训练脚本深入探讨
我们微调 e5-large-v2 其中最重要的是 MTEB 基准测试 使用 PEFT-LoRA。
句子嵌入的自动模型
返回查询和产品嵌入,以及
均值池
函数在序列维度上对它们进行池化并对它们进行标准化:
class AutoModelForSentenceEmbedding(nn.Module):
def \_\_init\_\_(self, model\_name, tokenizer, normalize=True):
super(AutoModelForSentenceEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.normalize = normalize
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
def forward(self, \*\*kwargs):
model_output = self.model(**kwargs)
embeddings = self.mean_pooling(model_output, kwargs["attention\_mask"])
if self.normalize:
embeddings = torch.nn.functional.normalize(embeddings, p=2, dim=1)
return embeddings
def mean\_pooling(self, model\_output, attention\_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] # First element of model\_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
def \_\_getattr\_\_(self, name: str):
"""Forward missing attributes to the wrapped module."""
try:
return super().__getattr__(name) # defer to nn.Module's logic
except AttributeError:
return getattr(self.model, name)
def get\_cosine\_embeddings(query\_embs, Product\_embs):
返回 torch.sum(query_embs * Product_embs, axis=1)
def get\_loss(cosine\_score, labels):
return torch.mean(torch.square(labels * (1 - cosine_score) + torch.clamp((1 - labels) * cosine_score, min=0.0)))
这
get_cosine_embeddings
函数计算余弦相似度和
获取损失
函数计算损失。该损失使模型能够了解到余弦分数为
1
查询和产品对是相关的,余弦分数为
0
或以下无关紧要。
定义 PeftConfig 使用您的 LoRA 超参数,并创建一个 PeftModel 。我们使用 🤗 Accelerate 来处理所有设备管理、混合精度训练、梯度累积、WandB 跟踪以及保存/加载实用程序。
结果
下表比较了训练时间、Colab 中适合的批量大小以及 PEFT 模型和完全微调模型之间的最佳 ROC-AUC 分数:
| Training Type | Training time per epoch (Hrs) | Batch Size that fits | ROC-AUC score (higher is better) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Trained e5-large-v2 | - | - | 0.68 |
| PEFT | 1.73 | 64 | 0.787 |
| Full Fine-Tuning | 2.33 | 32 | 0.7969 |
PEFT-LoRA 模型火车 1.35X 更快并且更适合 2X 与完全微调的模型相比,批量大小有所下降,并且 PEFT-LoRA 的性能与完全微调的模型相当,相对下降了 -1.24% 在 ROC-AUC 中。正如中提到的,这个差距可能可以用更大的模型来弥补 参数高效提示调整的规模力量 。
推理
我们走吧!现在我们有了模型,我们需要为目录中的所有产品创建搜索索引。
请参阅
peft_lora_embedding_semantic_similarity_inference.ipynb
获取完整的推理代码。
1.获取我们可以调用的产品的id列表
ids_to_products_dict
:
{0: 'RamPro 10" All Purpose Utility Air Tires/Wheels with a 5/8" Diameter Hole with Double Sealed Bearings (Pack of 2)',
1: 'MaxAuto 2-Pack 13x5.00-6 2PLY Turf Mower Tractor Tire with Yellow Rim, (3" Centered Hub, 3/4" Bushings )',
2: 'NEIKO 20601A 14.5 inch Steel Tire Spoon Lever Iron Tool Kit | Professional Tire Changing Tool for Motorcycle, Dirt Bike, Lawn Mower | 3 pcs Tire Spoons | 3 Rim Protector | Valve Tool | 6 Valve Cores',
3: '2PK 13x5.00-6 13x5.00x6 13x5x6 13x5-6 2PLY Turf Mower Tractor Tire with Gray Rim',
4: '(Set of 2) 15x6.00-6 Husqvarna/Poulan Tire Wheel Assy .75" Bearing',
5: 'MaxAuto 2 Pcs 16x6.50-8 Lawn Mower Tire for Garden Tractors Ridings, 4PR, Tubeless',
6: 'Dr.Roc Tire Spoon Lever Dirt Bike Lawn Mower Motorcycle Tire Changing Tools with Durable Bag 3 Tire Irons 2 Rim Protectors 1 Valve Stems Set TR412 TR413',
7: 'MARASTAR 21446-2PK 15x6.00-6" Front Tire Assembly Replacement-Craftsman Mower, Pack of 2',
8: '15x6.00-6" Front Tire Assembly Replacement for 100 and 300 Series John Deere Riding Mowers - 2 pack',
9: 'Honda HRR Wheel Kit (2 Front 44710-VL0-L02ZB, 2 Back 42710-VE2-M02ZE)',
10: 'Honda 42710-VE2-M02ZE (Replaces 42710-VE2-M01ZE) Lawn Mower Rear Wheel Set of 2' ...
2.使用经过培训的 smangrul/peft_lora_e5_ecommerce_semantic_search_colab 获得产品嵌入的模型:
# base model
model = AutoModelForSentenceEmbedding(model_name_or_path, tokenizer)
# peft config and wrapping
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)
device = "cuda"
model.to(device)
model.eval()
model = model.merge_and_unload()
import numpy as np
num_products= len(dataset)
d = 1024
product_embeddings_array = np.zeros((num_products, d))
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(dataloader)):
with torch.no_grad():
with torch.amp.autocast(dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_type="cuda"):
product_embs = model(**{k:v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}).detach().float().cpu()
start_index = step*batch_size
end_index = start_index+batch_size if (start_index+batch_size) < num_products else num_products
product_embeddings_array[start_index:end_index] = product_embs
del product_embs, batch
- 使用 HNSWlib 创建搜索索引:
def construct\_search\_index(dim, num\_elements, data):
# Declaring index
search_index = hnswlib.Index(space = 'ip', dim = dim) # possible options are l2, cosine or ip
# Initializing index - the maximum number of elements should be known beforehand
search_index.init_index(max_elements = num_elements, ef_construction = 200, M = 100)
# Element insertion (can be called several times):
ids = np.arange(num_elements)
search_index.add_items(data, ids)
return search_index
product_search_index = construct_search_index(d, num_products, product_embeddings_array)
- 获取查询嵌入和最近邻:
def get\_query\_embeddings(query, model, tokenizer, device):
inputs = tokenizer(query, padding="max\_length", max_length=70, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
query_embs = model(**{k:v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}).detach().cpu()
return query_embs[0]
def get\_nearest\_neighbours(k, search\_index, query\_embeddings, ids\_to\_products\_dict, threshold=0.7):
# Controlling the recall by setting ef:
search_index.set_ef(100) # ef should always be > k
# Query dataset, k - number of the closest elements (returns 2 numpy arrays)
labels, distances = search_index.knn_query(query_embeddings, k = k)
return [(ids_to_products_dict[label], (1-distance)) for label, distance in zip(labels[0], distances[0]) if (1-distance)>=threshold]
- 让我们用查询来测试一下 《深度学习书籍》 :
query = "deep learning books"
k = 10
query_embeddings = get_query_embeddings(query, model, tokenizer, device)
search_results = get_nearest_neighbours(k, product_search_index, query_embeddings, ids_to_products_dict, threshold=0.7)
print(f"{query=}")
for product, cosine_sim_score in search_results:
print(f"cosine\_sim\_score={round(cosine\_sim\_score,2)} {product=}")
输出:
query='deep learning books'
cosine_sim_score=0.95 product='Deep Learning (The MIT Press Essential Knowledge series)'
cosine_sim_score=0.93 product='Practical Deep Learning: A Python-Based Introduction'
cosine_sim_score=0.9 product='Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems'
cosine_sim_score=0.9 product='Machine Learning: A Hands-On, Project-Based Introduction to Machine Learning for Absolute Beginners: Mastering Engineering ML Systems using Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow'
cosine_sim_score=0.9 product='Mastering Machine Learning on AWS: Advanced machine learning in Python using SageMaker, Apache Spark, and TensorFlow'
cosine_sim_score=0.9 product='The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book'
cosine_sim_score=0.89 product='Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems'
cosine_sim_score=0.89 product='Machine Learning: A Journey from Beginner to Advanced Including Deep Learning, Scikit-learn and Tensorflow'
cosine_sim_score=0.88 product='Mastering Machine Learning with scikit-learn'
cosine_sim_score=0.88 product='Mastering Machine Learning with scikit-learn - Second Edition: Apply effective learning algorithms to real-world problems using scikit-learn'
尽管深度学习和机器学习的书籍被检索
机器学习
未包含在查询中。这意味着该模型已经了解到这些书籍在语义上与基于亚马逊上客户的购买行为的查询相关。
理想情况下,接下来的步骤将涉及使用 ONNX/TensorRT 来优化模型并使用 Triton 服务器来托管它。看看🤗 最佳 进行相关优化以实现高效服务!

